Nutritional Content of Cheddar Cheese Sticks: Cheddar Cheese Stick Nutrition
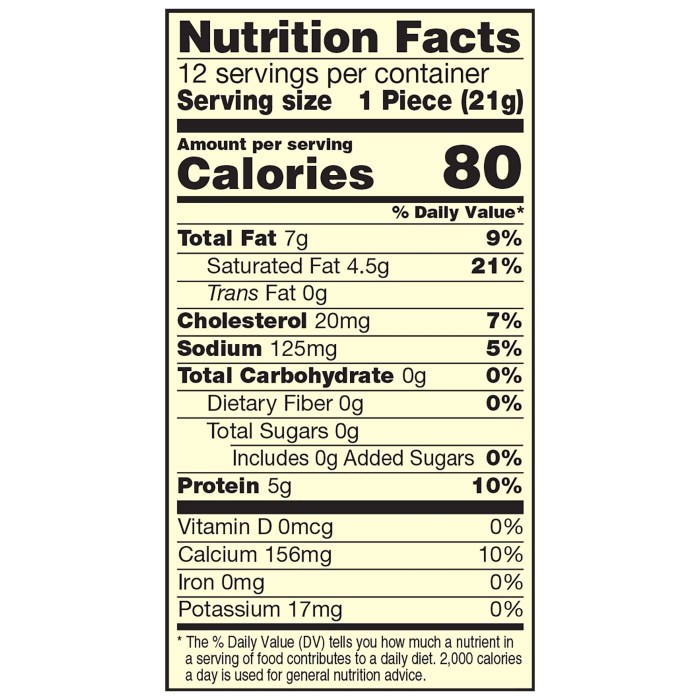
Cheddar cheese stick nutrition – Cheddar cheese sticks offer a convenient and portable source of protein and calcium, but their nutritional profile can vary significantly depending on the brand and specific ingredients used. Understanding the macronutrient and micronutrient composition is crucial for making informed dietary choices. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the typical nutritional content found in a single serving of cheddar cheese stick.
Macronutrient Composition of Cheddar Cheese Sticks
A typical 1-ounce (approximately 28-gram) cheddar cheese stick provides a significant amount of protein and fat, with minimal carbohydrates. The exact amounts can fluctuate based on the manufacturing process and the type of milk used. However, a reasonable estimate for a standard serving includes approximately 7 grams of protein, 8 grams of fat, and 1 gram of carbohydrate.
The high fat content contributes significantly to the caloric density, with a single stick typically containing around 80-100 calories. It’s important to note that saturated fat constitutes a considerable portion of the total fat content.
Micronutrient Profile of Cheddar Cheese Sticks
Cheddar cheese sticks are a good source of several essential micronutrients. The following table summarizes the vitamin and mineral content, which can again vary based on the brand and manufacturing process. These values represent average ranges and should not be considered absolute.
| Nutrient | Amount (per 1-ounce serving) | % Daily Value (DV) (Approximate) | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium | 150-200mg | 15-20% | Essential for bone health and muscle function. |
| Phosphorus | 150-200mg | 15-20% | Supports bone health, energy production, and cell function. |
| Vitamin A | 10-20% DV | 10-20% | Supports vision, immune function, and cell growth. |
| Vitamin D | 2-5% DV | 2-5% | Crucial for calcium absorption and bone health. |
| Vitamin K2 | Trace amounts | Variable | Important for bone health and cardiovascular health. |
| Vitamin B12 | 0.5-1 mcg | 2-8% | Essential for nerve function and red blood cell formation. |
Variations in Nutritional Content Across Brands
The nutritional content of cheddar cheese sticks can vary considerably among different brands. Some brands may use milk with higher fat content, resulting in a higher calorie and fat count. Others might add additional ingredients, such as whey protein or other flavorings, which can alter the macronutrient and micronutrient profiles. For example, some brands might fortify their cheese sticks with extra calcium or vitamin D, leading to higher percentages of the daily recommended values.
Always check the nutrition label on the specific product to get the most accurate information for your chosen brand. Reading the ingredient list is also essential to identify any potential allergens or additives.
Cheddar Cheese Sticks vs. Other Dairy Snacks
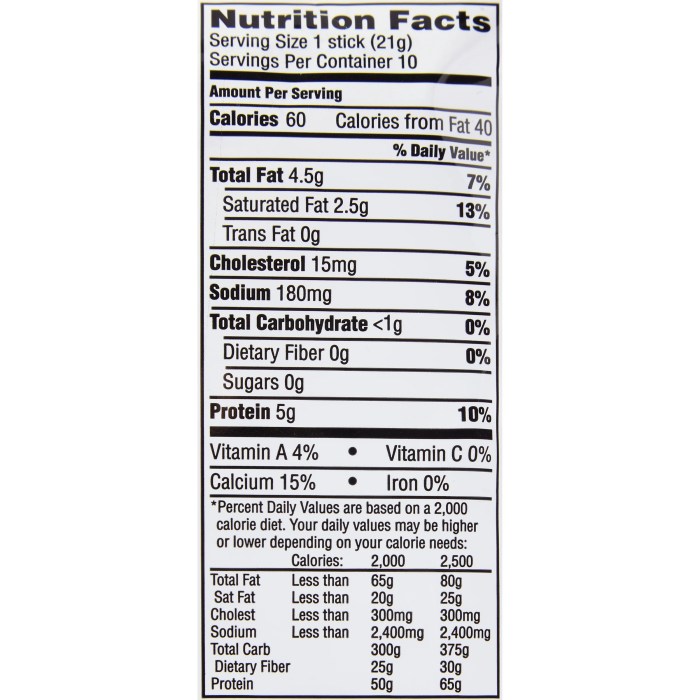
Cheddar cheese sticks offer a convenient and palatable source of dairy, but how do they stack up against other popular dairy snacks in terms of nutritional value? This section compares and contrasts cheddar cheese sticks with yogurt, string cheese, and milk, highlighting their respective advantages and disadvantages to help you make informed choices about your snacking habits.
A direct comparison reveals significant differences in macronutrient profiles and micronutrient content across these dairy options. Understanding these variations is crucial for making dietary choices that align with individual nutritional needs and goals.
Nutritional Comparison of Dairy Snacks
The following table provides a side-by-side comparison of the nutritional content of cheddar cheese sticks, yogurt, string cheese, and milk. Note that values can vary depending on brand and specific product formulation. This table uses average values for a standard serving size.
| Nutrient | Cheddar Cheese Stick (approx. 1 oz) | Yogurt (approx. 6 oz) | String Cheese (approx. 1 oz) | Milk (approx. 8 oz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calories | 70-80 | 100-150 | 70-80 | 100-120 |
| Protein (g) | 6-7 | 10-15 | 7-8 | 8-9 |
| Fat (g) | 5-6 | 0-5 | 6-7 | 2-8 (varies greatly by fat content) |
| Carbohydrates (g) | 1-2 | 15-20 | 1-2 | 12-13 |
| Calcium (mg) | 150-200 | 200-300 | 150-200 | 300-350 |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cheddar Cheese Sticks, Cheddar cheese stick nutrition
Choosing between cheddar cheese sticks and other dairy snacks involves weighing various factors. Here’s a breakdown of the advantages and disadvantages of opting for cheddar cheese sticks.
- Advantages: Portability and convenience are key advantages. Cheddar cheese sticks are readily available, require no preparation, and are easy to transport. They also provide a good source of protein and calcium.
- Disadvantages: Cheddar cheese sticks are relatively high in fat compared to yogurt or low-fat milk. They are also lower in carbohydrates and often lack the probiotic benefits found in yogurt.
In contrast, yogurt offers a higher protein content and often contains probiotics beneficial for gut health, while string cheese provides a similar nutritional profile to cheddar cheese sticks but might be perceived as less messy. Milk, depending on its fat content, offers a balance of nutrients but may not be as portable or convenient.
Serving Size and Portion Control

Cheddar cheese sticks, while a convenient and tasty source of protein and calcium, require mindful consumption to align with overall dietary goals. Understanding appropriate serving sizes and employing effective portion control strategies are crucial for managing calorie intake and maintaining a balanced diet. This section will provide guidance on appropriate serving sizes for various demographics and offer practical strategies for incorporating cheddar cheese sticks into a healthy eating plan.Appropriate Serving Sizes for Different Age Groups and Activity LevelsServing sizes for cheddar cheese sticks should be adjusted based on individual needs, considering age, activity level, and overall caloric requirements.
A general guideline is to consider the nutritional information provided on the packaging, which typically indicates a serving size and the corresponding calories, fat, and protein content. Children will require smaller portions compared to adults, and those with higher activity levels may need slightly larger portions to meet their energy needs. For example, a young child might consume one cheese stick as a snack, while a teenager involved in sports might consume two.
Always consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized dietary advice.
Strategies for Portion Control
Several strategies can help manage cheddar cheese stick consumption and prevent overeating. Pre-portioning cheese sticks into individual snack bags can facilitate mindful consumption. Alternatively, measuring the serving size using a food scale or measuring cup can provide accurate portion control. Being mindful of hunger cues and paying attention to satiety signals can also help regulate intake. It is also important to consider the overall dietary intake for the day, and to ensure that the cheese sticks are not contributing significantly to excessive calorie or fat intake.
Choosing lower-fat options when available can further support portion control efforts.
Incorporating Cheddar Cheese Sticks into a Balanced Diet
Cheddar cheese sticks can be easily incorporated into a balanced diet as part of a snack or meal. They can be paired with fruits like apples or grapes for a balanced snack providing both protein and carbohydrates. They can also be included in a lunchbox with vegetables such as carrot sticks or cucumber slices. For a more substantial meal, cheddar cheese sticks can complement a salad, adding a protein boost.
Cheddar cheese sticks, a convenient snack, offer a quick dose of calcium and protein. However, considering the overall nutritional profile, it’s interesting to compare them to a heartier breakfast like a steak egg and cheese bagel nutrition , which provides more substantial energy. Ultimately, choosing between them depends on your individual dietary needs and the context of your meal.
The fat content in both, though, should be considered when making a choice.
However, it’s important to remember that while cheese sticks offer some nutritional value, they shouldn’t be the primary source of nutrients. A balanced approach, combining them with other nutritious foods, is key. For instance, a lunchbox could include a cheddar cheese stick, a whole-wheat sandwich, and a side of baby carrots and cherry tomatoes, providing a good balance of protein, carbohydrates, and fiber.
Visual Representation of Nutritional Information
Visual aids are crucial for effectively communicating complex nutritional data. Clear and concise visuals help consumers quickly understand the nutritional composition of cheddar cheese sticks and compare them to other snacks. Effective visual representations can significantly improve consumer understanding and informed food choices.
Macronutrient Composition of a Cheddar Cheese Stick
To create a visual representation of the macronutrient composition of a cheddar cheese stick, consider a pie chart. This chart would divide a circle into segments representing the proportions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. The size of each segment would be directly proportional to the percentage of each macronutrient. For example, if a cheddar cheese stick contains 20% protein, 30% fat, and 50% carbohydrates (these are illustrative percentages and may vary depending on the brand and specific product), the protein segment would occupy 20% of the circle, the fat segment 30%, and the carbohydrate segment 50%.
Each segment should be clearly labeled with the macronutrient name and its percentage. Using distinct and easily distinguishable colors for each segment will enhance clarity. A legend clarifying the color-coding should also be included.
Comparison of Cheddar Cheese Sticks and Other Dairy Snacks
A bar graph is an ideal visual representation to compare the nutritional profiles of cheddar cheese sticks with similar snacks like string cheese, yogurt, or cottage cheese. The horizontal axis would list the different snacks, while the vertical axis would represent the quantity of each nutrient (e.g., grams of fat, protein, or carbohydrates per serving). For each snack, separate bars would represent the amount of fat, protein, and carbohydrates.
Using different colors for each nutrient will help distinguish them easily. This allows for a direct visual comparison of the relative amounts of each macronutrient across the different snacks. The graph should include a clear title and axis labels, as well as a legend to identify the color-coding of each nutrient. Adding data labels to the bars can further improve readability by displaying the exact numerical values.
Quick FAQs
Are cheddar cheese sticks suitable for children?
In moderation, yes. However, parents should monitor their children’s intake due to the sodium and saturated fat content. Smaller portions are recommended for younger children.
Can cheddar cheese sticks be part of a weight-loss diet?
They can be, but portion control is crucial. Their calorie and fat content should be factored into daily caloric intake goals. Choosing lower-fat varieties can also help.
Are all cheddar cheese sticks created equal nutritionally?
No, nutritional content varies significantly depending on the brand and specific ingredients used. Checking nutrition labels is essential.
What are some healthier alternatives to cheddar cheese sticks?
Greek yogurt, string cheese (lower sodium options), and hard-boiled eggs offer similar protein and calcium benefits with potentially lower saturated fat and sodium.
