Ingredients and Processing of Kraft Cheese Slices

Kraft cheese slices nutrition – Kraft cheese slices, a ubiquitous staple in many refrigerators, undergo a complex manufacturing process involving several ingredients and steps that ultimately impact their nutritional profile. Understanding these aspects is crucial for consumers seeking to make informed dietary choices.
Ingredients in Kraft Cheese Slices
The precise ingredient list can vary slightly depending on the specific flavor and product line. However, the core components remain consistent. The following table details typical ingredients, their purpose, and potential health implications. It’s important to note that the quantities are approximations and can vary based on the specific product formulation.
| Ingredient | Quantity (Approximate) | Purpose | Potential Health Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Milk | Major Component | Provides protein, calcium, and fat | Source of essential nutrients; high fat content may contribute to weight gain if consumed excessively. |
| Cheese Cultures | Small Amount | Ferment milk, contributing to flavor and texture | Generally considered safe; some individuals may have sensitivities. |
| Salt | Moderate Amount | Enhances flavor, acts as a preservative | Excessive sodium intake can contribute to high blood pressure. |
| Whey | Variable | Binds ingredients, adds moisture | Generally considered safe; contributes to lactose content. |
| Sodium Phosphate | Small Amount | Emulsifier, prevents separation | High intake may affect mineral absorption. |
| Other Additives (e.g., colorings, preservatives) | Small Amounts | Enhance appearance, extend shelf life | Potential for allergic reactions or other adverse effects; generally used in amounts considered safe by regulatory bodies. |
Processing Methods and Nutritional Content
Kraft cheese slices are produced through a process that involves several steps. First, milk is pasteurized and then fermented with cheese cultures. The resulting curd is then cooked and separated from the whey. This mixture is then blended with other ingredients, including salt, emulsifiers, and preservatives. The final blend is then shaped into slices, often using a molding process, and finally packaged.The processing methods, particularly the addition of emulsifiers and preservatives, can impact the nutritional content.
For example, the addition of salt significantly increases the sodium content. Also, some processing techniques might reduce the bioavailability of certain nutrients. While the precise changes in nutritional content are difficult to generalize without specific product analysis, it’s clear that processing alters the nutritional profile compared to the raw ingredients.
Kraft cheese slices, those ubiquitous squares of processed dairy, offer a quick, albeit processed, protein boost. However, a comparison with the nutritional profile of other cheeses is often insightful; for instance, checking out detailed cottage cheese nutrition info reveals a stark contrast in fat and protein content. Ultimately, understanding both helps make informed choices about incorporating cheese into one’s diet, especially when considering the long-term impact of processed versus unprocessed dairy products on one’s health.
Additives and Preservatives in Kraft Cheese Slices, Kraft cheese slices nutrition
Several additives and preservatives are typically included in Kraft cheese slices to enhance flavor, texture, and shelf life. These may include sodium phosphate, various emulsifiers, and artificial colors. While generally considered safe by regulatory bodies in the amounts used, some individuals may have sensitivities or allergies to these additives. For instance, individuals with lactose intolerance might experience digestive discomfort due to the lactose present in whey.
Similarly, those sensitive to sodium may need to monitor their intake carefully. The potential long-term health implications of regular consumption of these additives remain a subject of ongoing research.
Health Considerations and Potential Concerns
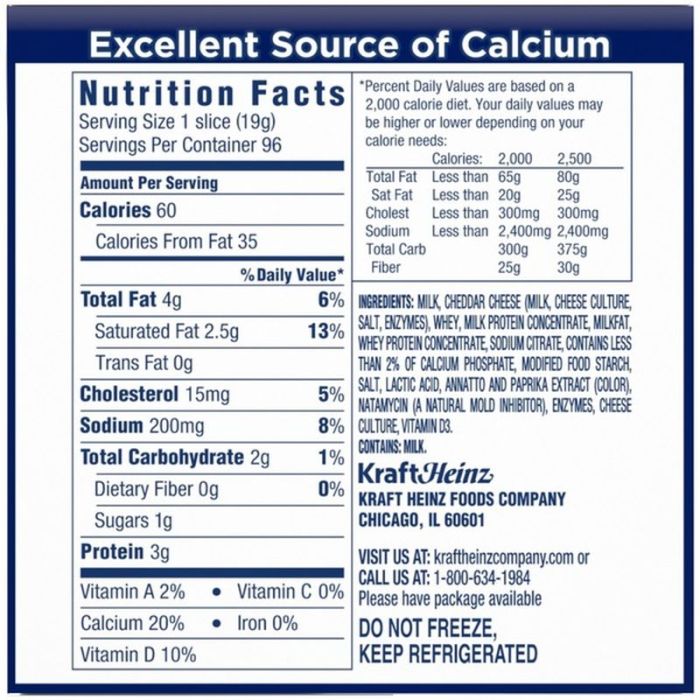
Kraft cheese slices, while convenient and appealing to many, present some potential health concerns related to their nutritional profile. Regular consumption, particularly in larger quantities, may contribute to an increased intake of sodium and saturated fat, both of which are linked to various health issues. Understanding these concerns allows for informed choices regarding their inclusion in a balanced diet.The high sodium content in Kraft cheese slices is a significant consideration.
Sodium intake is a major factor in blood pressure regulation, and excessive sodium consumption is a known risk factor for hypertension. Similarly, the relatively high saturated fat content contributes to elevated cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. These factors, coupled with the cheese slices’ relatively low fiber and micronutrient content compared to some alternative protein sources, highlight the need for mindful consumption.
Sodium and Saturated Fat Content in Kraft Cheese Slices
A single slice of Kraft cheese typically contains a substantial portion of the recommended daily sodium intake. For example, one slice might contain approximately 150mg of sodium, contributing significantly to the recommended daily limit of 2,300mg for most adults. Similarly, the saturated fat content can contribute to an individual’s daily saturated fat limit, potentially leading to elevated LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol) if consumed regularly in excess.
This is particularly relevant for individuals already at risk of cardiovascular issues.
Visual Representation of Nutrient Proportions
Imagine a pie chart representing the daily recommended intake of various nutrients. One slice of Kraft cheese would occupy a relatively large segment representing sodium and saturated fat. A smaller segment would illustrate the contribution of protein, while calcium and other micronutrients would be represented by even smaller segments. The remaining, significantly larger portion of the chart would depict the remaining daily intake needed from other food sources to achieve a balanced nutritional profile.
This visual representation highlights the significant contribution of sodium and saturated fat from a single serving and the need to supplement with nutrient-rich foods to maintain overall dietary balance.
Recommendations for Mindful Consumption
Mindful consumption of Kraft cheese slices can mitigate potential health risks. Here are some key recommendations:
- Limit consumption: Restrict intake to one or two slices per day, and spread consumption throughout the week rather than consuming several slices in one sitting.
- Balance with nutrient-rich foods: Pair cheese slices with foods high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals to create a more balanced meal. This could include whole-grain crackers, fruits, or vegetables.
- Choose lower-sodium options: Explore reduced-sodium or lower-fat varieties of cheese slices if available, to reduce the intake of sodium and saturated fat.
- Consider alternatives: Occasionally substitute Kraft cheese slices with other protein sources, such as lean meats, beans, nuts, or other cheeses with a more favorable nutritional profile.
- Monitor overall diet: Pay attention to the overall sodium and saturated fat content of your diet, ensuring that Kraft cheese slices don’t significantly contribute to exceeding recommended daily limits.
FAQ Explained: Kraft Cheese Slices Nutrition
Are Kraft cheese slices a good source of calcium?
Yes, they do contain calcium, but the amount varies depending on the variety. Check the nutrition label for specific values.
Can I eat Kraft cheese slices if I’m lactose intolerant?
Kraft offers lactose-free cheese slices, but some individuals with severe lactose intolerance may still experience symptoms. Always check the ingredients and consider alternatives.
How many Kraft cheese slices should I eat per day?
This depends on your individual calorie needs and dietary goals. Moderation is key, as they are relatively high in sodium and saturated fat.
Are there healthier alternatives to Kraft cheese slices?
Yes, many natural cheeses offer similar protein and calcium content with less sodium and saturated fat. Consider cheddar, mozzarella, or other varieties.
