Feta Cheese and Dietary Considerations
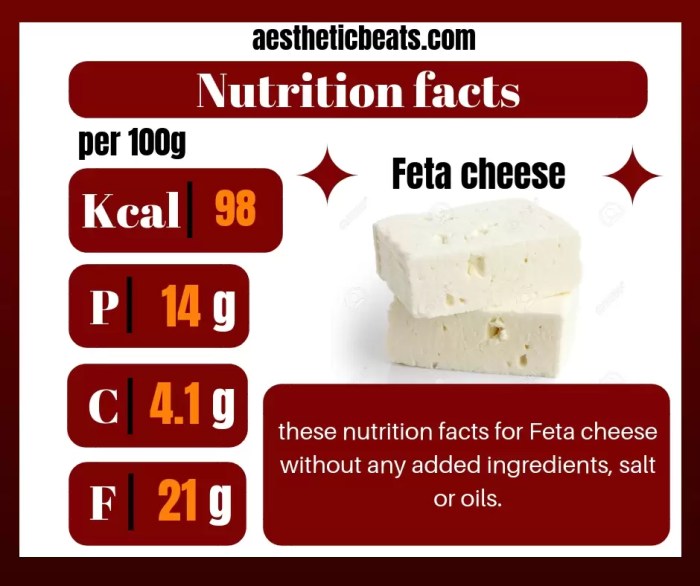
Nutrition facts of feta cheese – Feta cheese, a beloved staple in Mediterranean cuisine, presents a unique nutritional profile that necessitates careful consideration for individuals adhering to specific dietary restrictions or seeking to optimize their health. Its high fat and sodium content, alongside its potential allergen profile, requires a nuanced understanding to ensure safe and beneficial consumption. This section will examine the suitability of feta cheese within various dietary frameworks, highlight potential allergens, and explore the associated health benefits and risks.
Feta Cheese and Specific Diets, Nutrition facts of feta cheese
The nutritional composition of feta cheese makes it a less-than-ideal choice for some diets, while offering potential benefits within others. Understanding these nuances is crucial for informed dietary planning.
So, you’re checking out feta cheese’s nutritional profile? It’s pretty salty, right? But let’s be real, sometimes you crave that cheesy goodness, and comparing it to something like, say, the kraft macaroni and cheese nutrition facts , is a total eye-opener. You’ll see how feta’s fat and sodium content stacks up. Then you can make the best choice for your next beachside chill sesh!
- Low-Sodium Diet: Feta cheese is naturally high in sodium. Individuals on a low-sodium diet should significantly limit or avoid feta cheese consumption due to its potential to exceed daily sodium recommendations. Alternatives like low-sodium cheeses or reduced-sodium versions (if available) may be considered, but these may compromise the distinctive flavor profile of feta.
- Low-Fat Diet: Feta cheese is a relatively high-fat food. While it contains some beneficial fatty acids, individuals following a low-fat diet should consume it sparingly. The fat content can contribute to increased calorie intake, potentially hindering weight management goals. Consider using smaller portions or opting for lower-fat alternatives, though this may alter the texture and taste.
- Ketogenic Diet: Feta cheese can be a suitable addition to a ketogenic diet. Its high fat content aligns with the diet’s emphasis on fat intake, while its moderate protein content contributes to satiety. However, sodium content should still be monitored. A serving of feta cheese can be a flavorful addition to keto-friendly meals.
- Vegetarian Diet: Feta cheese is naturally suitable for vegetarians, as it is a dairy product and does not contain any meat or animal-derived products. It provides a good source of protein and calcium within a vegetarian diet.
Feta Cheese Allergens and Sensitivities
While generally well-tolerated, feta cheese can pose risks for individuals with specific allergies or sensitivities.
- Dairy Allergy: The most significant allergen in feta cheese is casein, a milk protein. Individuals with dairy allergies should strictly avoid feta cheese as it can trigger allergic reactions ranging from mild digestive upset to severe anaphylaxis.
- Lactose Intolerance: Feta cheese contains lactose, a milk sugar. Individuals with lactose intolerance may experience digestive discomfort after consuming feta, although the lactose content varies depending on the aging process. Aged feta tends to have lower lactose levels than fresh feta.
Health Benefits and Risks of Feta Cheese Consumption
Regular consumption of feta cheese offers potential health benefits but also carries certain risks.
- Benefits: Feta cheese is a source of calcium, important for bone health. It also provides protein, contributing to muscle building and repair. Furthermore, it contains some beneficial fatty acids.
- Risks: High sodium content can contribute to hypertension and cardiovascular problems. High fat content can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. The potential for allergic reactions in susceptible individuals should not be overlooked.
Types and Variations of Feta Cheese

Feta, that salty, tangy crumbly delight, isn’t just one thing. Its character, both in taste and nutritional profile, shifts subtly depending on the milk source and the cheesemaking process. Understanding these variations allows for a more informed choice, whether you’re a feta fanatic or a curious newcomer.
The most significant factor influencing feta’s characteristics is the type of milk used. While sheep’s milk is traditionally the star, goat’s milk and even cow’s milk are increasingly common, each contributing a unique flavor and nutritional fingerprint.
Milk Source and Nutritional Differences
The milk source dramatically alters the final product’s nutritional composition. Sheep’s milk feta generally boasts a higher fat content and a richer, more complex flavor than goat’s milk feta. Cow’s milk feta, often the least expensive option, tends to have a milder taste and a lower fat content. These differences are reflected in the following table:
| Milk Type | Fat Content (Approximate) | Protein Content (Approximate) | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sheep’s Milk | 20-30% | High | Sharp, tangy, complex |
| Goat’s Milk | 15-25% | High | Tangy, slightly less sharp than sheep’s milk |
| Cow’s Milk | 10-20% | Moderate | Milder, less tangy |
Note: These are approximate values and can vary significantly depending on the specific brand, production methods, and animal diet.
Production Methods and Nutritional Impact
The production methods employed, specifically pasteurization and aging, subtly influence the nutritional makeup of feta. Pasteurization, a heat treatment killing harmful bacteria, might slightly reduce the levels of certain heat-sensitive nutrients. However, it also ensures food safety, a critical consideration. Aging, on the other hand, affects the texture and flavor, potentially influencing the protein breakdown and the development of certain beneficial compounds.
Longer aging periods often result in a firmer, more intensely flavored cheese. The impact on the overall nutritional value, however, is usually minimal.
Fat Content Variations Across Brands
The fat content in feta can vary considerably between brands, even within the same milk type. Factors like the breed of animal, their diet, and the specific cheesemaking techniques all contribute to this variability. For instance, a sheep’s milk feta from a small, artisanal producer might have a higher fat content than a mass-produced version. Consumers should always check the nutrition label to understand the fat content of their chosen brand.
For example, Brand A’s sheep’s milk feta might list 28% fat, while Brand B’s might show only 22%, even though both are sheep’s milk feta. This highlights the importance of careful label reading.
FAQs: Nutrition Facts Of Feta Cheese
Is feta cheese suitable for a low-carb diet?
While feta cheese contains carbohydrates, the amount is relatively low, making it suitable for many low-carb diets, particularly ketogenic diets, when consumed in moderation.
How does feta cheese compare to other cheeses in terms of sodium content?
Feta cheese is generally higher in sodium than some other cheeses like mozzarella or cheddar. Individuals on low-sodium diets should monitor their intake carefully.
Can feta cheese be frozen?
Freezing feta cheese can alter its texture, making it crumbly. While feasible, it’s generally recommended to use fresh feta for optimal taste and texture.
What are some good substitutes for feta cheese?
Depending on the recipe, alternatives include goat cheese, ricotta cheese, or even a mixture of cream cheese and lemon juice for a similar tang.
